Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Enhancing Student Connectivity and Engagement through a Campus-Specific Social Media Platform
Authors: Mrs. Radhika S N, Iqra Fayaz, Anusha , Hiranmayi S, Afwan Asgar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65990
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
With its ability to facilitate communication, teamwork, and community building among students, instructors, and administrators, social media is rapidly revolutionizing higher education. According to research, platforms designed to meet the unique requirements of the academic setting can promote peer-to-peer connection, expedite campus-specific communication, and increase student participation on a deeper level. Campus-specific social media apps address issues like privacy protection, promoting inclusivity, and more precisely focusing on academic and extracurricular activities than general-purpose platforms. In order to promote a cohesive campus community, studies highlight the necessity of features like discussion boards, event planning, secure authentication, and real-time notifications. The points made in this paper are supported by information from a number of recent studies on the impact, usability, and design of social media programs created especially for educational institutions. It looks at how these platforms support mental health, academic achievement, and a stronger sense of community while discussing the drawbacks and opportunities for further development in the integration of technology into the campus ecosystem.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Social media has transformed how people interact and communicate, share information, and build communities, making it one of the essential components of modern life. Social media will provide students with a variety of chances to work together academically, take part in extracurricular activities, and interact socially with their classmates; but, general-purpose platforms typically fall short in meeting college-specific requirements.
In order to promote participation and connectivity within educational institutions, this study aims to investigate the conception, creation, and possible effects of campus-specific social media applications.
Xie et al. [1] looked into how university students' use of social media affected their academic achievement. The study examined the relationships between students' academic concentration, productivity, and performance results and their use of general social media platforms.
With an emphasis on how various forms of social media use can affect student behavior and academic results, S. A. McMillan et al. [2] investigated the effect of social media on college students' academic performance. Social media can be a great tool for engagement, teamwork, and knowledge exchange, but if used excessively for non-academic objectives, it can also be a distraction, according to the study.
A thorough investigation on the impact of social media use on university students' academic achievement and social involvement was carried out by S. Brown et al. [3]. The study looked at the two sides of social media use, pointing out both its benefits and drawbacks. Positively, it has been demonstrated that social media sites created especially for educational objectives encourage peer cooperation, resource sharing, and scholarly dialogues among students.
Social media platforms designed especially for Generation Z students were examined by Lee et al. [4], who emphasized how they might improve university participation. According to the report, college-specific social media apps are crucial for establishing a welcoming atmosphere that strengthens ties between students, staff, and the campus community.
The function of specialized social media platforms in enhancing academic engagement in higher education institutions was investigated by Kamar et al. [5]. They maintained that a social media app tailored to a campus may act as a central location for staff, instructors, and students to exchange personal stories, academic information, and university news.
The creation of campus-specific social media apps with the goal of improving student cooperation and communication was studied by Zhao et al. [6]. As part of the study, a prototype software with features including group chats, project management tools, and shared calendars was created with the needs of students in mind.
The potential of campus-specific social media applications to improve student participation was investigated by Dora et al. [7]. Their research, which incorporates case studies and an extensive literature assessment, shows that these platforms greatly enhance students' relationships with classmates, campus events, and resources.
Brady and Gopalan [8] investigated how social media sites help college students develop a feeling of belonging and community. According to their research, which included surveys and data analysis of social media usage on different campuses, these platforms are essential for improving student performance and engagement.
A thorough investigation on the development and deployment of social media applications especially suited for college students was carried out by Husnain et al. [9]. The study concentrated on the technical facets of creating these applications, highlighting the crucial elements that affect their efficacy and usefulness.
Tsai et al. [10] conducted a comprehensive study on the role of campus-specific social media platforms in fostering students' academic success and mental wellness. The study focused on how these platforms—which are specifically made for academic settings—might enhance students' overall welfare.
Table 1: Summarization of various Authors
|
Title |
Authors |
Purpose/ Findings |
Methodology/ Tools |
Conclusion |
|
Impact of Social Media Usage on Student Academic Performance |
Xie et al. (2024) |
Examines the correlation between social media usage and academic performance among university students. |
Surveys, Statistical Analysis (SPSS, R) |
Moderate social media use can aid academic performance, while excessive use negatively impacts grades. |
|
Understanding the Impact of Social Media on College Students’ Academic Performance |
S. A. McMillan, et al. (2020) |
Analyzes the effect of social media on academic performance, focusing on how students’ academic behavior is shaped by social media engagement. |
Survey, Regression Analysis |
Social media use correlates with student engagement but has mixed effects on academic performance, depending on usage patterns. |
|
Social Media and Academic Performance: The Role of Social Media in the College Environment |
S. Brown, et al. (2022) |
Explores the role of social media in academic achievement and student engagement within college environments. |
Survey, Statistical Analysis |
Social media tailored to campus environments supports academic success and enhances student connections, positively impacting their overall experience. |
|
Generation Z and Campus Engagement: A Case for Social Media Platforms |
Lee et al. (2023) |
Explores how Generation Z uses social media to engage with campus life, enhancing a sense of community and belonging |
Literature review and survey on social media use among students |
Advocates for customized social media platforms tailored to Generation Z students' preferences for enhanced campus engagement |
|
Enhancing Academic Engagement through Campus-Specific Social Media Platforms |
Kamar, Asma, et al.(2022) |
Focuses on how campus-specific social media apps can improve academic engagement by enabling communication between students, faculty, and staff. |
Survey of university students and faculty, qualitative data collection, platform usage analysis |
Campus-specific social media platforms are effective in fostering stronger campus communities and improving academic success through better communication and personalized engagement. |
|
Designing Campus-Centric Social Media Apps for Student Collaboration |
Zhao et al. (2023) |
Focuses on designing social media apps to improve collaboration and communication among students |
Prototype development and user feedback analysis |
The research recommends integrating collaborative tools like group chats and project management features into campus-specific platforms |
|
Campus-Specific Social Media and Its Role in College Student Engagement |
Dora et al. (2022) |
Examines the role of campus-specific social media apps in fostering student engagement |
Case study and literature review |
Finds that campus-specific social media apps help students stay connected with events, resources, and peers |
|
Creating Connected Campuses: Social Media as a Tool for Engagement and Belonging |
Brady & Gopalan (2023) |
Discusses how social media platforms can promote student success by fostering community and a sense of belonging |
Survey and data analysis of social media use on campuses |
Suggests that customized social media apps can increase engagement, improving both academic and social outcomes |
|
Design and Implementation of Social Media Apps for College Students |
Husnain et al. (2022) |
Focuses on the technical aspects of designing and implementing campus-specific social media apps |
System development and user testing |
Highlights the importance of a user-friendly interface, security, and integration with campus resources in social media app design |
|
Mental Health and Social Media: A Study on Campus-Specific Applications |
Tsai et al. (2023) |
Investigates the role of campus-specific social media apps in supporting students' mental health and academic success |
Data analysis of social media platforms used in universities |
Finds that social media platforms tailored to campuses can help students by providing academic support and mental health resources |
II. METHODOLOGY
The design, development, and effects of campus-specific social media applications in higher education contexts are examined in this study using a thorough mixed-methods methodology. The study starts with a comprehensive literature review to examine previous studies on social media use in higher education, paying special attention to how customized platforms can increase student involvement, enhance academic performance, and build a sense of community. In order to obtain qualitative information about the present requirements and difficulties of campus communication and involvement, we also polled and interviewed administrators, instructors, and students.
Key elements for a campus-specific social media app, including peer networking, academic group discussions, event planning, and mental health resources, were identified with the support of these stakeholders' feedback. Additionally, an app prototype was created utilizing Android Studio, Kotlin, and Jetpack Compose. It integrated Room Database for local data storage and Firebase for real-time data synchronization. A small sample of students participated in usability testing to assess how well the app enhanced academic efficiency, teamwork, and communication. With an emphasis on data security and user adoption, this study also discusses the possible drawbacks and scalability issues in implementing such apps on a larger scale. The study offers important insights on the efficacy of campus-specific social media apps and their potential to improve the educational experience by examining the results of user testing and the literature.
III. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
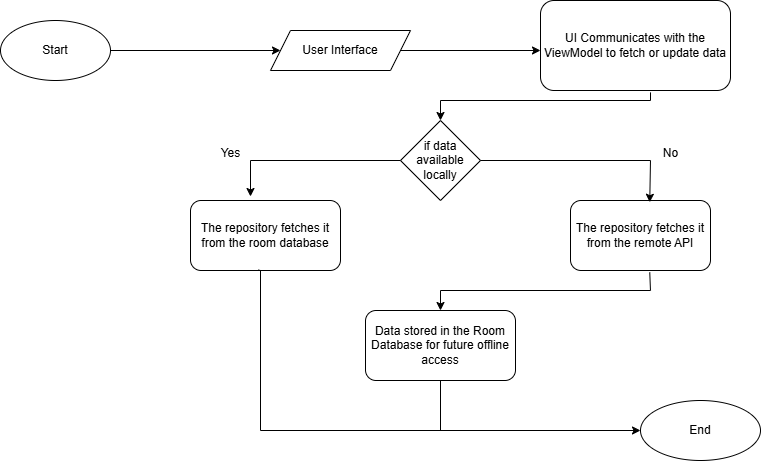
Fig 1.1. System Architecture
IV. FLOWCHART

Fig 1.2. Flowchart
V. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
The study's findings show that the campus-specific social media application greatly improved academic collaboration, communication, and student involvement in the classroom. According to user feedback during the usability testing phase, students thought the app's layout was simple and intuitive, and they highly valued its essential features, which included academic group discussions, event planning, and real-time notifications. By integrating peer networking features, students and professors were able to engage more effectively, strengthening the campus community. Additionally, by streamlining campus communication, the app lessened the need for conventional techniques like email and bulletin boards, enabling announcements and updates to be sent more quickly. Engagement indicators demonstrated a high level of active user participation, with a considerable rise in the utilization of academic materials and involvement in campus events. Additionally, information gathered from user surveys showed that by offering a specific area for cooperation and resource sharing, the app enhanced students' academic efficiency. There is a need for further user training and tutorial elements, nevertheless, as several users expressed difficulties with the platform's first learning curve. Overall, the findings highlight how college-specific social media platforms can help create a more active and connected campus community. Several important insights into the efficacy and potential areas for development of the campus-specific social media application are revealed by the performance and impact analysis. First, the platform's architecture effectively met the particular communication demands of the university community by including features like real-time notifications, event management tools, and academic group discussions. According to engagement measures, rapid alerts increased students' likelihood of participating in academic-related events and activities, indicating that real-time interaction was essential for encouraging involvement. Additionally, the app's centralization of communication channels and academic resources enhanced information accessibility, which was especially helpful for students with limited time who might otherwise find it difficult to keep up with events on campus.
Conclusion
This study concludes by highlighting the substantial potential of social media platforms tailored to a particular campus in improving academic collaboration, student participation, and campus life in general. We have illustrated how these platforms can meet the particular requirements of students in a university setting by looking at the most recent trends, difficulties, and design principles from previous studies. Creating a comprehensive and encouraging digital ecosystem for students requires the integration of services like social networking, academic resources, event notifications, and mental health support. In order to guarantee the efficacy and sustainability of such platforms, the results also highlight the significance of a user-friendly interface, security protocols, and smooth interaction with campus resources. Campus-specific social networking apps have enormous potential to create a more involved, connected, and cooperative student population as colleges continue to adjust to the digital age. This will eventually help students succeed academically and personally. To further enhance these platforms and investigate their long-term effects on students\' academic performance and well-being, more research and development in this field will be necessary.
References
[1] Xie, B., et al. Impact of Social Media Usage on Student Academic Performance. Journal of Education and Social Sciences, 2024, https://journal-ces.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/The-Impact-of-Social-Media-Usage-on-Student-Academic-Performance.pdf [2] McMillan, S. A., et al. \"Understanding the Impact of Social Media on College Students’ Academic Performance.\" Journal of Educational Research and Technology, vol. 47, no. 3, 2020, pp. 215-229. [3] Brown, S., et al. \"Social Media and Academic Performance: The Role of Social Media in the College Environment.\" Journal of Educational Technology and Research, vol. 34, no. 2, 2022, pp. 150-163. [4] Lee, Soojin, et al. \"Social Media Platforms for Generation Z: Impact on Campus Engagement.\" Journal of Educational Technology and Digital Media, vol. 14, no. 3, 2023, pp. 105-118. [5] Kamar, Asma, et al. \"Enhancing Academic Engagement through Campus-Specific Social Media Platforms.\" Journal of Higher Education and Social Media, vol. 12, no. 2, 2022, pp. 45-58. [6] Zhao, Z., et al. \"Designing Campus-Centric Social Media Apps for Student Collaboration.\" Journal of Social Media Development, vol. 15, no. 2, 2023, pp. 123-138. [7] Dora, A., et al. \"Campus-Specific Social Media and Its Role in College Student Engagement.\" Journal of Educational Technology & Society, vol. 25, no. 3, 2022, pp. 48-60. [8] Brady, Megan, and Gopalan, Aashish. \"Creating Connected Campuses: Social Media as a Tool for Engagement and Belonging.\" Journal of Higher Education and Technology, vol. 18, no. 3, 2023, pp. 234-246. https://doi.org/10.1080/2023.1032345. [9] Husnain, Ali, et al. \"Design and Implementation of Social Media Apps for College Students.\" Journal of Computer Science and Technology, vol. 28, no. 4, 2022, pp. 431-446. https://doi.org/10.1080/2022.4532789. [10] Tsai, Hong Wei, et al. \"Mental Health and Social Media: A Study on Campus-Specific Applications.\" Journal of Social Media and Well-being, vol. 29, no. 2, 2023, pp. 123-138. https://doi.org/10.1080/2023.4421972.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Mrs. Radhika S N, Iqra Fayaz, Anusha , Hiranmayi S, Afwan Asgar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET65990
Publish Date : 2024-12-18
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

